Abortion was legalised in 2002, yet in 2016 only 41 percent of women knew that abortion was legal and only half (51%) of abortions were carried at authorised sites . An estimated 323,000 abortions were performed in Nepal in 2014, a rate of 42 abortions per 1,000 women aged 15–49 years, compared to 37 per 1,000 in Bangladesh where abortion is legal and 50
per 1,000 in Pakistan where abortion is only available in limited circumstances. There is some evidence that sex-selective abortion may be becoming more common. The expected sex ratios at birth are 105 males per 100 female births, yet data from surveys and the census indicate that Province 1, Province 7 and Province 5 all have sex ratios at birth of over 120 males per 100 females . Comparison between the 2016 and 2011 NDHSs indicates that the skewedness of the sex ratio has been consistently high for males in Province 5.
Table of Contents
Abortion Service Status
Only 13.6 percent of health facilities offer normal vaginal delivery services and comprehensive abortion care, whereas more facilities (25.9%) offer vaginal delivery services and medical abortion services. Government hospitals are more likely to offer comprehensive abortion care services than private hospitals. Yet women do use the private sector: of those women who had an abortion in 2016, for example, 31 percent used a government facility, 27 percent used a private facility, 13 percent a NGO facility and 27 percent of women bought abortion medicine and took the medicine at home. Seventy-two percent of women who have had an abortion used medical (non-surgical) abortion. The 2014 study referenced above estimates that 323,000 abortions were performed in Nepal. A 2016 survey reported that nine percent of women said their pregnancies ended in
induced abortion, which implies that there could be significant underreporting of abortion. Province 1 (7%) and Province 2 (5%) have the lowest rates of pregnancies ending in abortion. For women aged 35–49 years, 27 percent of pregnancies ended in induce abortion. Half of these women (50.3%) who had an abortion did not want more children but of these women, only 51.9 percent were provided with information on FP and 25.2 percent used a FP method within two weeks of having the abortion . Repeat abortion may be becoming more common. A nationally representative survey indicates that in 2016
only 0.4 percent of women of reproductive age had an abortion at least twice, whereas a study of two clinics in Kathmandu covering over 1,000 women, indicated that 32 percent of women had repeat abortions with the incidence rising with age and parity
Milestone of Abortion Services in Nepal

Facts about Abortion
- There are no SDG targets for abortion
- Abortion was legalized in 2002 yet only half of abortions are carried out in authorized sites
- 41 percent of women aged 15–49 are aware that abortion is legal
- Nine percent of all pregnancies (15–49) and 27 percent of pregnancies to women aged 35–49 end in abortion
- Fourteen percent of health facilities that offer normal vaginal delivery services also offer comprehensive abortion care; twenty-six percent offer vaginal delivery services and medical abortion services, with government hospitals more likely to offer these services than private hospitals
- Medical abortion is the most popular method of abortion
- Of women who had an abortion, 51.9 percent were provided with information on FP and 25.2 percent used a FP method within two weeks of having the abortion
- The law prohibits sex-selective abortion yet there is evidence that sex ratios at sub-national levels are becoming skewed
Management of Abortion and Post-Abortion Care in Nepal

of Provider:
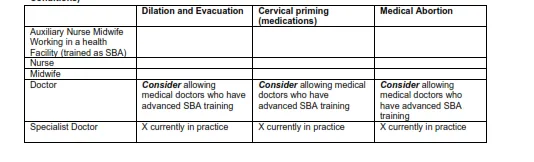
from 12 to 28 Weeks in Cases of Rape and Incest, Risk to Maternal and Foetal Health and Maternal Mental
Conditions)
Recommend Further References and Downloads
- National Safe Abortion Policy 2002 – Download
- Free Safe Abortion Service guideline 2073 – Download
- NEPAL SAFE MOTHERHOOD AND NEWBORN HEALTH ROAD MAP 2030 – Download
Post that might Interest you
- Webinar on World Hand Hygiene | Register today

- World’s First 5-in-1 vaccine against meningitis | Men5CV

- World Health Worker Week 2024 | Know theme

- World Autism Awareness Day 2024 | Know theme

- Staff Nurse | OCH | latest jobs vacancy 2024

- World Hepatitis Summit 2024 | WHO

- Staff Nurse | TLMN | ngo jobs 2024

- World Health Day 2024 | Know theme

- Measuring access to assistive technology in Nepal | Country Report

bachelor jobs bph jobs covid19 health health for all health guidelines new health jobs healthjobs healthjobs in nepal health jobs vacancy health public health update ingo jobs jobs after passing bachelor jobs for bph jobs in nepal jobs in ngo ngo jobs ngo jobs vacancy ngo jobs vacancy for bph ngo job vacancy 2021 nurse jobs nurse jobs 2021 nurse vacancy nursing insurance nursing job nursing jobs nursing jobs 2021 nursing jobs in nepal nursing law nursing officer Nursing Vacancy Public health Public health concern public health important days Public health in Nepal publichealth jobs public health updated Staff Nurse Staff Nurse and HA Vacancy | Nepal Army 2021 staff nurse vacancy staff nurse vacancy in ngo 2021 nepal staff nurse vacancy kathmandu who guidelines WHO official

Hey there, I am Nirdesh Baral, founder of Nepal Health Magazine. I am a Tech geek by passion , Public health practitioner by profession and an Ailurophile by heart and a patriot by birth



