Rapid Assessment of Socio Economic Impact of COVID19 in Nepal | UNDP – The uncertain impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on Nepal’s social economy will magnify depending on how events unfold on three fronts: first, its dependence on tourism, trade, and foreign employment – and the consequences that will propagate through the services and industrial landscape; second, if or when the spread of the pandemic overwhelms a grossly inadequate health infrastructure and antivirals or vaccine become available; and third, Nepal’s heavy geo-economic reliance on India and China, and the nature of contagion in those countries.
Based on a painstaking survey of 700 businesses and 400 individuals, and consultations with over 30 private sector
organizations and government agencies, conducted tenaciously during the lockdown, we find that the COVID-19
pandemic has disrupted supply chains, shut or threatened the survival of small and informal enterprises, and made
people highly vulnerable to falling back into poverty through widespread loss of income and jobs.
Accommodation and food; arts, entertainment and recreation; and transport are the three most affected sectors of the economy. Given the international travel restrictions and fall in discretionary
disposable incomes worldwide, tourism receipts in Nepal are projected to decline by 60 percent in 2020 resulting in a loss of foreign currency earnings worth US$400 million. Similarly, the fall in remittances is likely to range between 15 and 20 percent this fiscal year. The cumulative impact of trade, tourism and remittance shocks – as well as the negative economic externalities they trigger in allied sectors
Nepal’s projected pre-COVID-19 GDP growth rate of 8.5 percent will plunge to well below 2.5 percent in 2019-2020, and severely constrain a rebound in 2020-2021.
Both formal and informal MSMEs are hit hard as they tend to have low cash-to-asset ratios. We find that three in five employees have lost their jobs in the micro- and small businesses that were surveyed. Those businesses have seen a fall of 95 percent in average monthly revenue. They can sustain for only around two months if the lockdown continues. Cash subsidies from the government was ranked as the most important form of support expected from economic stimulus, followed by subsidies on interest rates, concessional loans, and rental waivers by landlords. Subsidies on utility payments were considered the least important support needed by small and informal businesses.
Table of Contents
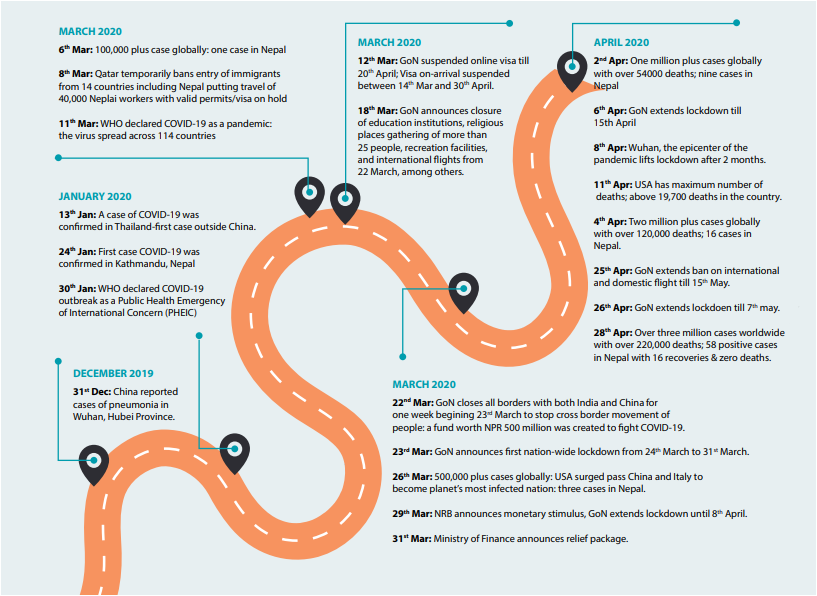
COVID-19 roadmap
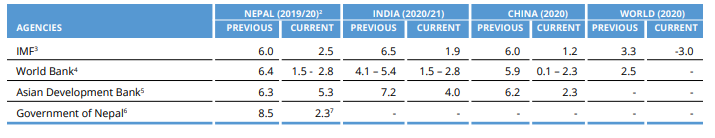
Macroeconomic status
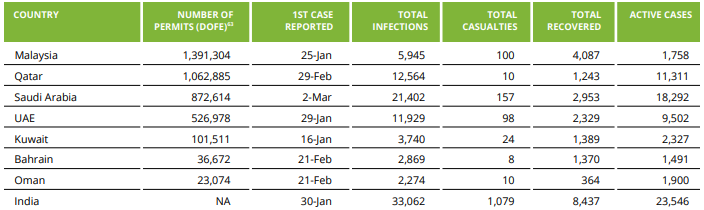
STATUS OF COVID-19 IN NEPALI MIGRANT WORKERS’ KEY DESTINATION COUNTRIES
During the lockdown, Karnali Province still earned the lowest average revenue of NPR 1,600, which translated to a loss of 99 percent. While significant, Gandaki province and Province 1 lost around 83 percent of their average revenue during the lockdown– less than otherprovinces.
STRUCTURAL CHALLENGES
The country lacks adequate healthcare facilities and infrastructure. Government investment in health care
is suboptimal. In private hospitals, charges are high for the average person. There are also questions over the reliability and safety of medical treatment in the country. So those that can afford to often prefer to travel abroad (mainly to India) for treatment.
Nepal shares an open and porous land-border with India of more than 1,700 km. Communities either side of the border are closely linked socially and culturally. For this reason, Nepal has remained economically dependent on India. In recent decades, even essential goods and services that could otherwise have been produced locally are being imported. The open border has also given criminals and fugitives from both sides opportunities to escape the law.
Nepal has a history of low economic growth and high inflation. The economy is further strained by an unholy trinity of high prices, low productivity and high domestic consumption. It has lost its competitiveness in many important
sectors, including agriculture and manufacturing. Domestic consumption is high – around 87.5
percent per annum in the last 10 years. It is because of remittances that the national savings rate is high, which in turn has supported capital
COPING STRATEGY DURING THE LOCKDOWN BY TYPE OF EMPLOYMENT
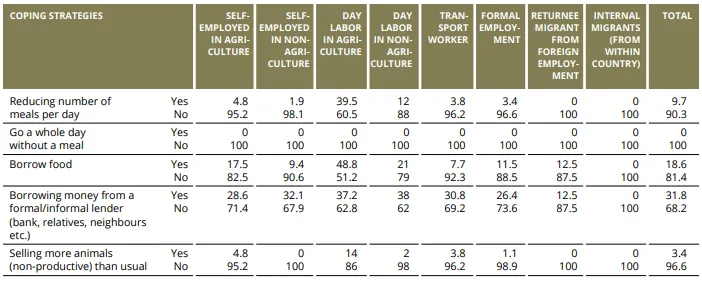
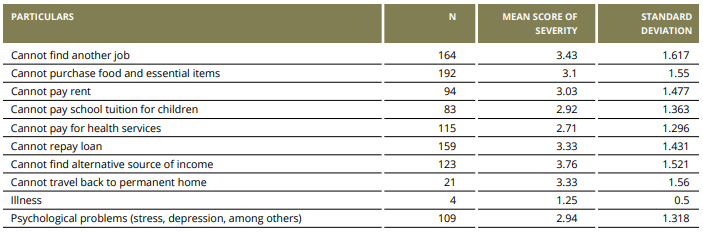
IMPACT OF COVID-19 ON INDIVIDUAL

Hey there, I am Nirdesh Baral, founder of Nepal Health Magazine. I am a Tech geek by passion , Public health practitioner by profession and an Ailurophile by heart and a patriot by birth



